1
Formerly of Hunting Land & Environment Limited, a division of HTS Development Ltd. (HTS)
, Thamesfield House, Boundary Way, Hemel Hempsted, Hertfordshire HP2 7SR
2
Environmental Archaeology Unit (EAU), University of York, York, YO10 5DD
3
City of York Council (CYC),
Planning and Design,
City of York Council,
9 St Leonards Place,
York,
YO1 7ET
4
York Archaeological Trust (YAT),
Cromwell House,
13 Ogleforth,
York,
YO1 7FG
M.Davies mat.cath@dial.pipex.com,
A. Hall biol8@york.ac.uk,
H. Kenward biol6@york.ac.uk,
J. Oxley john.oxley@york.gov.uk,
David Brinklow dbrinklow@yorkarchaeology.co.uk
The City of York Council has been pursuing a strict policy of in situ preservation of archaeological deposits since April 1990. Planning consent is normally granted in the historic core of York for a new development so long as less than 5% of the archaeological deposits that are preserved on a site are destroyed.
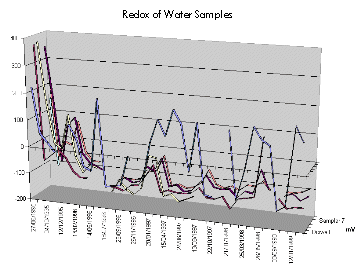
During archaeological evaluation work carried out as part of the redevelopment and expansion proposals for Marks & Spencer plc on Parliament Street, deposit monitoring devices were installed to investigate and monitor both the character of the archaeological deposits present and also the burial environment surrounding them (of particular importance because the burial environment, in terms both of its characteristics and stability, is thought to play a vital role in the preservation in situ of a site's archaeological deposits). The monitoring programme was undertaken between June 1995 and April 1998. As a result the data from a total of 30 site visits have been collected and are presented in this report.

This article discusses results of the deposit monitoring project and presents evidence of changes that appear to be taking place in the archaeological deposits. Although the lower deposits at Parliament Street are stable, the upper deposits show considerable seasonal variations.
The concept of preservation of archaeological deposits in situ is now deeply embedded both in Codes of Professional Conduct (IFA Code of Conduct) and in national policy guidance (PPG 16). However, this emphasis on preservation in situ has been criticised. Does conservation archaeology in general and the City of York policy in particular achieve the preservation of the remaining 95% of the archaeology? Or are these deposits condemned to unseen, unrecorded destruction, sealed below new buildings; indeed if this is the case, shouldn't these deposits be excavated now while they are still viable?
Go to Article Table of Contents
© Internet Archaeology / Author